The armed forces and biodiversity
The French ministry of the Armed Forces manages a total of 275,000 hectares of land, a large part of which is used for military training. Military land, access to which is regulated, has escaped urban sprawl, certain intensive farming methods and industrial development and therefore often harbours a remarkable and interesting range of fauna and flora:
- 200,000 hectares of military land are concerned by at least one biodiversity classification areas (ZNIEFF (Natural Zone of Interest for Ecology, Flora and Fauna), Natura 2000, etc.)
- 20% of military land is included in the European biodiversity protection network, “Natura 2000”.

Titre : Entrainement militaire
Source : © SGA Com
Natura 2000 and military land

What is Natura 2000 ?
Natura 2000 is the name of a network of sites of ecological interest in the European Union identified for the rarity of their species of wild animals and plants and their habitats. The designation of a site as a Natura 2000 site is based on objectives relating to:
of the Natura 2000 network are on military land! That amounts to almost 1/5th of the total area occupied by the French ministry of the Armed Forces!
- the conservation and preservation of natural habitats and particularly remarkable species of fauna and flora
- the reconciliation of human activities with issues linked to biodiversity
Two European Directives underpin what is the world’s largest network of protected area:
- the 1979 Birds Directive, which defines Special Protection Areas (SPAs)
- the Habitats Directive, which defines Special Areas of Conservation (SACs) for flora and fauna
These SPAs and SACs form what is known as the Natura 2000 network.
Today the Natura 2000 network consists of :
Natura 2000 sites in Europe
of the land in the European Union and 6% of the area covered by the seas around it
Natura 2000 sites in France
of the land surface of Metropolitan France (i.e., some 7 million hectares) and 33% of the marine area
The French ministry of the Armed Forces and the network of Conservancies of Natural Areas

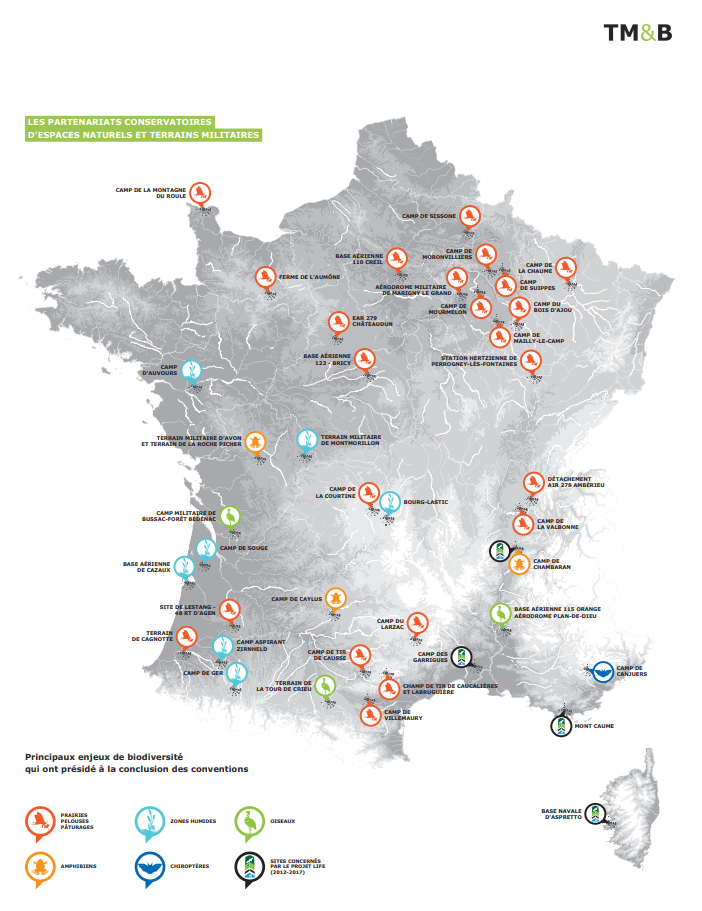
To preserve the biodiversity of its sites and ensure government policy on biodiversity is followed, the French ministry of the Armed Forces has set up a number of ecology partnerships.
The Federation of Conservancies of Natural Areas (FCEN) is one of the French ministry of the Armed Forces ‘ most important and oldest ecology partners.
The first local partnership agreements between Conservancies of Natural Areas (CENs) and military sites date back to the 1990s. Initially, the initiatives were only local, but then the collaboration between the armed forces and the CENs took on a national dimension with the signing of a framework agreement in 2009, which was renewed in 2015 for a further 10 years.
Aware of the wealth of ecological biodiversity to be found on military land, the CENs offer their expertise and know-how to the French ministry of the Armed Forces with the aim of preserving this remarkable biodiversity. By providing tools and tailored solutions developed in consultation with the camps, the CENs are able to help them reconcile the operational functions of the military sites with the preservation of their biodiversity. This is one of the main reasons that the collaboration has been such a success!
More specifically, this partnership has also provided the structure to run the LIFE programmes in conjunction with military sites: LIFE Défense Nature 2Mil from 2012 to 2017, LIFE NaturArmy and LIFE La Valbonne since 2019.
Some key figures illustrating the partnership between the military sites and the network of CENs:
- 1st local partnership in 1991 (Marigny-le-Grand aerodrome – CEN Champagne-Ardenne)
- A 12-year-long partnership at national level
- 52 military camps managed with the CENs, covering over 80,000 hectares (including 18,000 under Natura 2000)
- 3 LIFE programmes on military sites run in partnership with the network of Conservancy of Natural Areas (CENs)
The French ministry of the Armed Forces ' other ecology partners
LPO, the French society for the protection of birds
A memorandum of understanding was signed with the LPO in 2011 and renewed in 2018, which set up a joint programme of actions (avian fauna inventories, national action plans on endangered species, avian fauna observatories at the MINARM sites and participation in the LPO’s refuge programme).
The MINARM and LPO are also working together on the preservation of the bearded vulture, a species that is the subject of a national action plan. A protocol on this species was renewed in 2021.
The National Natural History Museum (MNHN)
The Museum is a recent partner (2019) of the MINARM. This partnership is complementary to the LIFE NaturArmy programme and provides for the development of a method to evaluate the biodiversity on military sites and devise a strategy for collecting biodiversity data. The objective of the partnership is to arrive at a model of ecological management that is efficient and adaptable to all the military sites, thereby contributing to the Ministerial biodiversity strategy as planned by the LIFE NaturArmy programme.
The project partners









